*This post may contain affiliate links. Read more.*
Introduction
In the quest for effective weight management and optimal health, high-protein, low-calorie meals have gained widespread attention. Research consistently shows that protein plays a crucial role in metabolism, muscle preservation, and satiety. But what does the science actually say? How can you incorporate these meals into your daily routine for maximum benefit? This article explores the evidence behind high-protein, low-calorie diets and provides practical insights for sustainable nutrition.
1. The Role of Protein in Metabolism and Weight Management
Protein is a macronutrient that requires more energy to digest compared to fats and carbohydrates. This process, known as the thermic effect of food (TEF), can enhance metabolism and increase calorie expenditure. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that protein-rich meals can increase energy expenditure by 15-30%, compared to only 5-10% for carbohydrates and 0-3% for fats.
Additionally, high-protein diets have been linked to reduced cravings and better appetite control. Protein influences the secretion of hunger hormones such as ghrelin and peptide YY, leading to increased feelings of fullness. This can naturally reduce calorie intake, making weight loss and maintenance more sustainable.
2. Muscle Retention and Fat Loss: Why Protein Matters
When reducing calorie intake, the risk of losing muscle mass increases. Maintaining adequate protein intake helps preserve lean muscle while encouraging fat loss. According to research in The Journal of Nutrition, individuals who followed a high-protein, calorie-restricted diet retained more muscle mass compared to those consuming a low-protein diet.
For those engaged in strength training or resistance exercises, consuming high-protein, low-calorie meals can significantly improve muscle recovery and growth. Essential amino acids, particularly leucine, stimulate muscle protein synthesis, preventing muscle breakdown and promoting strength.
3. Best High-Protein, Low-Calorie Foods to Include
Not all protein sources are created equal. The following foods are high in protein while remaining low in calories:
- Egg whites (17 calories, 3.6g protein per egg white)
- Greek yogurt (non-fat) (100 calories, 17g protein per serving)
- Chicken breast (120 calories, 26g protein per 3oz serving)
- Tofu (80 calories, 8g protein per 3oz serving)
- Lentils (116 calories, 9g protein per ½ cup cooked)
- Cottage cheese (low-fat) (90 calories, 12g protein per ½ cup)
- Salmon (wild-caught) (130 calories, 22g protein per 3oz serving)
Incorporating these foods into daily meals can help maintain a high-protein intake without excessive calorie consumption.
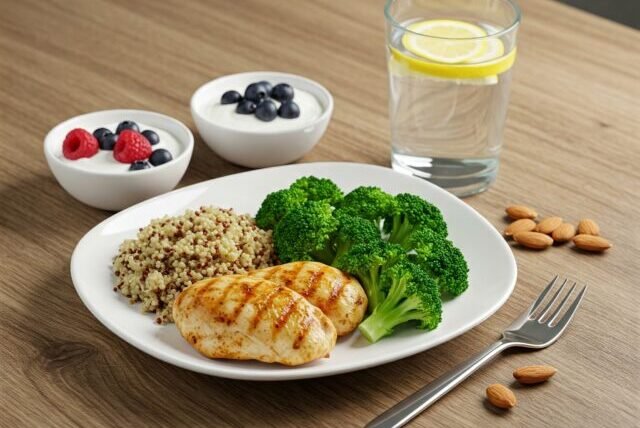
4. Sample High-Protein, Low-Calorie Meal Ideas
To put theory into practice, here are a few meal ideas that balance high protein and low calories:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with berries and a sprinkle of chia seeds (200-250 calories, 20g protein)
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with leafy greens, cherry tomatoes, and a lemon vinaigrette (300 calories, 35g protein)
- Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with steamed broccoli and cauliflower rice (350 calories, 30g protein)
- Snack: Cottage cheese with cinnamon and almonds (150 calories, 15g protein)
Conclusion
High-protein, low-calorie meals offer a science-backed approach to improving metabolism, retaining muscle, and controlling hunger. By incorporating protein-rich foods and balancing calorie intake, individuals can enhance their fitness goals, maintain a lean physique, and support overall health. Whether for weight loss, muscle maintenance, or simply better eating habits, understanding the role of protein in nutrition can lead to sustainable and effective dietary choices.
Start experimenting with these high-protein meal ideas today and experience the benefits firsthand!
#fitness nutrition #healthy eating #high-protein foods #low-calorie meals #metabolism #muscle retention #satiety #weight management