*This post may contain affiliate links. Read more.*
Food obsession is a complex issue that intertwines psychological, physiological, and emotional factors. It can manifest in compulsive thoughts about food, uncontrolled eating behaviors, and emotional dependence on food for comfort. This article explores the scientific basis of food obsession, emotional eating, and effective treatment approaches, including a personal experience with mindful eating techniques.
The Psychological and Physiological Aspects of Food Obsession
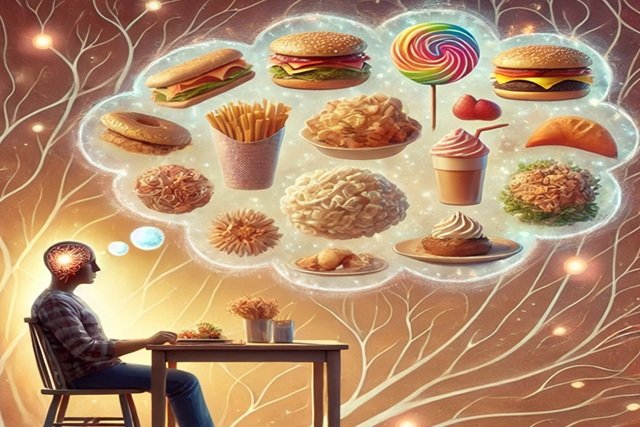
Food obsession often stems from a combination of psychological and physiological triggers. Studies suggest that compulsive eating behaviors may be linked to the brain’s reward system, particularly the release of dopamine when consuming high-sugar or high-fat foods (Volkow et al., 2013). This reward mechanism can create a cycle of craving and consumption, leading to an unhealthy relationship with food.
On the psychological side, food obsession is commonly associated with emotional distress, anxiety, and stress. Research indicates that individuals experiencing high levels of stress may turn to food as a coping mechanism, reinforcing habitual emotional eating patterns (Adam & Epel, 2007).
Emotional Eating: Understanding the Science
Emotional eating refers to consuming food in response to feelings rather than physical hunger. A study by Gibson (2012) highlights that negative emotions, such as sadness or loneliness, can increase cravings for energy-dense foods, leading to overconsumption and potential weight gain. Additionally, hormonal imbalances involving cortisol and ghrelin play a significant role in emotional eating behaviors (Cameron et al., 2018).
My Personal Experience with Mindful Eating
In my journey to understand food obsession, I experimented with mindful eating techniques. I focused on slowing down my meals, paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, and savoring each bite without distractions. Surprisingly, this simple practice made a profound difference. I found myself feeling more satisfied with smaller portions, reducing unnecessary cravings, and gaining greater control over emotional eating triggers.
Scientific research supports these findings. A study by Kristeller & Wolever (2011) found that individuals practicing mindful eating reported lower binge-eating tendencies and increased awareness of emotional triggers. This aligns with my personal experience of feeling more in tune with my body’s needs rather than responding to emotional impulses.
Treatment Approaches for Food Obsession
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – CBT has been extensively researched as an effective treatment for food obsession and binge eating. It helps individuals reframe negative thoughts about food and develop healthier coping mechanisms (Fairburn, 2008).
- Nutritional Guidance – Working with a registered dietitian can help establish balanced eating habits that prevent excessive food cravings.
- Mindful Eating – As I personally experienced, mindful eating techniques encourage greater awareness of hunger cues and emotional triggers, reducing impulsive eating behaviors.
- Stress Management – Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, exercise, or journaling can decrease emotional reliance on food (Kabat-Zinn, 1990).
- Support Groups and Therapy – Joining a support group or seeking therapy can provide valuable guidance and encouragement in overcoming food obsession.
Conclusion
Food obsession is a multifaceted issue influenced by psychological, physiological, and emotional factors. Scientific research highlights the role of the brain’s reward system, hormonal imbalances, and emotional triggers in developing unhealthy eating patterns. Through my own experience with mindful eating, I discovered that simple changes in eating habits can significantly impact food relationships. Combining scientific approaches with personal strategies, such as mindfulness and stress management, can provide long-term solutions for overcoming food obsession and achieving a balanced lifestyle.
#binge eating #coping mechanisms #dopamine and food #eating behaviors #eating habits #emotional eating #emotional triggers #emotional well-being #food cravings #food obsession #food relationship #healthy eating habits #healthy lifestyle #mental health #mindful eating #mindfulness #nutrition and mental health #physiological aspects #psychological triggers #stress eating #stress management